
Sustainable Supply Chain

Efficient integrated supply chain management is one of IRPC’s key strategies for sustainable business operation. IRPC makes great effort to manage our integrated supply chain efficiently, with consideration given to the environment, society, and principles of good corporate governance. IRPC aims to meet all expectations of our stakeholders in all processes throughout the supply chain, from raw material and crude procurement, general procurement, to logistic management. IRPC applies the use of technology to build a stable and effective foundation which further develops the potential of partners and customers to grow sustainably side-by-side.
Raw Material and Crude Procurement
Management Approach
Raw material procurement is a crucial process to IRPC’s operations. An efficient management system can ensure no impacts are made from any circumstances which may affect the crude and raw material procurement and cause business interruptions. IRPC has planned long-term and spot procurement of crude and raw materials to meet requirements, as well as risk management regarding price and cost of raw materials, logistics of crude and raw materials, and maintaining inventory.
General Procurement Management
Management Approach
IRPC prioritizes and focuses on the development of a sustainable procurement management system, which is one of the major strategies of the Procurement Department. Therefore, the system has been continuously developed by incorporating digital technology to support operational processes for efficient performance of users and suppliers. Suppliers can modify their own information in the system and update their products and services for more transactions between IRPC and suppliers. This also creates a channel for suppliers to communicate and comply with IRPC’s sustainable procurement guidelines. Furthermore, an ESG risk assessment was conducted on all tier 1 suppliers to jointly improve the potential of sustainable business operations. IRPC conducted a supplier satisfaction survey to analyze and enhance efficient operational processes.
IRPC has adapted the following digital technology to support operations under the Project PRO4.0:
- Demand Planning Platform, collecting demands for products from all departments with better accuracy, speed and sufficiently detailed for procurement planning.
- Spend Cube Analysis, enhancing the efficiency of procurement and lowering the cost of products.
- Process Workflow Redesign, improving the purchasing process to be faster and more efficient.
- Supplier Relationship Management (SRM) managing suppliers’ information including products or services available to IRPC and that from evaluation of potential suppliers.
Supply Chain Management
Management Approach
1. Policy
Regarding IRPC’s objective to promote Sustainable Procurement Excellence, IRPC is committed to carry out its procurement activities under five strategic initiatives: Smart Buyer, Data Management, Supplier Relationship Management (SRM), Sustainable Management, and Synergy and Collaboration.
|
2. Management System/Process
IRPC is highly committed to developing procurement strategy that focuses on product and service quality. Risk management processes are established to cover environmental, social, and governance (ESG) aspects in order to align management with risk level, while considering quality, quantity, and delivery of products and services. Other considerations include minimum compliance to labour laws, environmental laws, and other quality management systems to protect and mitigate risks that may impact quality, quantity, delivery of products and services, and trust of stakeholders in the company’s operations.
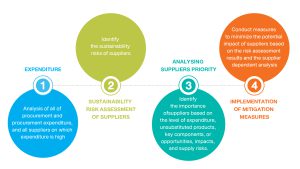
Suppliers ESG Program
Development of Supplier ESG Program is one initiative until IRPC’s Decarbonization Pathway of which approved and endorsed by Board of Directors. Moreover, the progress will be quarterly report to Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee as well as Board of Directors.
IRPC’s Decarbonization Pathway approved by Board of Directors [Link]
Training Program for Suppliers
In order to promote sustainable practices of procurement for our suppliers and networking, IRPC has set up training programs on their roles in the supplier ESG program provide for our suppliers including,
- Cubic Academy
- IRPC CG Day
- IRPC Supplier Conference
- Training prior to ESG audit
Supplier Sustainable Code of Conduct
IRPC is committed to conducting its business with fairness, legality and good corporate governance, coupled with social and environmental supports, in order to create balance in all aspects and live together sustainably. IRPC also publicly discloses our policies and encourages suppliers to implement policies along similar principles to extend IRPC’s commitment and vision to externally related operations. Therefore, to achieve mutual understanding, IRPC prepared a manual as a guideline for suppliers. It also require suppliers to operate under sustainable practices and have a Sustainable Procurement Policy in place. However, where suppliers choose not to comply with the manual, IRPC reserves the rights to take action against those suppliers as seen appropriate. Such actions will be determined based on possible impact and damages.
IRPC’s “Supplier Code of Conduct” covers all aspects of business such as business ethics, human rights, and safety health and environment. IRPC requires the code of conduct to be signed and complied with. Moreover, it also applies to enforce suppliers of suppliers to promote sustainable business values. The following requirements are covered in IRPC’s Supplier Code of Conduct:
- Environmental standards for the suppliers’ processes, products or services;
- Child labour prohibition;
- Other fundamental human rights (e.g. labour, freedom of association, ILO conventions);
- Working conditions (e.g. working hours, lay-off practices, remuneration);
- Occupational health and safety;
- Business ethics (e.g. corruption, anti-competitive practices); and
- Our suppliers should have a sustainable procurement policy in place for their own suppliers.
Furthermore, IRPC requires suppliers to adopt these requirements in order to enforce their suppliers (IRPC’s non-tier one suppliers) to follow these requirements as well.
IRPC has continually dedicated our efforts to improve the procurement system in order to enhance our international competitiveness. IRPC developed a procurement web portal to be used as a communication channel to suppliers regarding IRPC’s procurement requirements. The system provides suppliers with a convenient and fast tool to do business with IRPC and also allows for an end-to-end audit process of each procurement. The use of the e-Auction system from a third-party provider allows suppliers to freely compete with each other to offer their best price.
For more information download the Sustainability Sustainable Code of Conduct [link]
Supply Chain Awareness
IRPC prepares a spend analysis separately for feedstock of petroleum and petrochemical business, as well as general procurement for chemicals and components. Currently, there are two departments separately responsible for monitoring their own spending.The first department is a procurement function responsible for tracking the spending on chemicals, spare parts, and other related components.The second department is a feedstock function responsible for tracking spending on all types of refinery and petrochemical feedstock.
IRPC used a spend analysis to examine expenditure data with the purpose of reducing procurement costs, improving efficiency, and monitoring compliance. A critical analysis helps IRPC determine which suppliers are vital to IRPC’s business. IRPC analyses the importance of its suppliers and classifies them as Critical Suppliers if they meet the following criteria:
- High expenditure
- Covered critical parts/components
- Non-substitutable
- Strategic relationship.
Moreover, managing risk in the supply chain involves a supplier selection process and supplier risk management, which covers risks such as the quality of product and service, environmental, social and corporate governance. In order to conduct business with IRPC, suppliers are required to register and pass the pre-approval process and answer the self-assessment questionnaire.
Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) Risk Assessment
To mitigate any adverse impacts from the procurement process and to create a sustainable procurement system, IRPC conducts supplier/contractor risk assessments by identifying Economic, and Environmental, Social and Governance (ESG) risks. An ESG Risk Assessment focuses on identifying sustainability risks in the procurement process. For example, child and forced labor, and purchase of chemicals that contain prohibited substances. The risk assessment considers the likelihood of each issue and its impacts, using both qualitative and quantitative data, to the company and stakeholders.
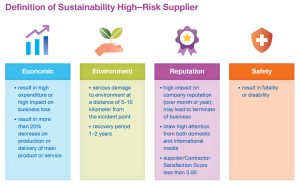
Significant Suppliers screening cover topics as follows;
- Environmental, i.e., ISO14001
- Social, i.e., international safety standards
- Governance, i.e., CAC membership
- Business relevance,i.e., expert, specialist consultant
Risk Management Measures
IRPC conducts root cause analyses and prepares risk treatment plans for sustainability high-risk suppliers. The Procurement Department closely monitors the progress of the risk treatment plans, to ensure appropriate deployment for reduced likelihood and/or impact to the level of risk appetite, and regularly requests an independent assessment to be carried out by the Internal Audit Office. The results of monitoring and control plans will be reported to the executives on a quarterly basis.
Supply Chain Risk Assessment and Corrective Action Plans
In addition to the risk management measures mentioned above, IRPC has, in place, a policy to promote and encourage suppliers to operate in line with IRPC’s sustainability development principles to mitigate risks and potential impacts from any wrong doings of suppliers to IRPC. Examples of the principles include: human rights, occupational health and safety, business ethics and conducts, as well as anti-corruption1. Therefore, to ensure that suppliers, including contractors, have and strictly adhere to such a policy, IRPC has regulated a supplier assessment as one of the necessary measures in the procurement process, allowing suppliers to assess their potential and answer a questionnaire related to aspects mentioned above.
To follow up on whether IRPC’s sustainability development principles and Code of Conduct have been applied and complied with. Audit topics include:
- Policy and Standards
- Business Integrity
- Business Ethics and Transparency
- Quality Standards
- Business Continuity/Interruption
- Society
- Human Rights
- Labour Relations
- Social Responsibility
- Occupational Health and Safety
- Security and Emergency Preparedness
- Environment
- Pollution Prevention and Resource Reduction
Together with non-conforming suppliers, Corrective action plans were provided to all supplier with high sustainability risk who have been through comprehensive assessment and found the non-conformity issues. IRPC prepares and agrees upon a corrective action plan. The non-conformity results were found in safety issues among contractors. Therefore, IRPC has immediately notified and provided the corrective action plans in order to prevent re-occurrence and to enable future improvement. As a result, all non-conformed auditees have finalized the corrective action plans to resolve issues and improve their ESG performance. IRPC also provided suggestions to those who passed the audit in order to improve their ESG performance.
ESG assessment committee [Link]
ESG assessment timeline [Link]
Integration of ESG factors into supplier selection
In order for suppliers to be included into IRPC’s approved vendor list, both new and existing suppliers must undergo a supplier evaluation. The ESG portion of the evaluation, based on key ESG objectives, consists of the following five criteria:
- To build awareness and an understanding of IRPC’s Sustainability Policy (Supplier Code of Conduct)
- To ensure that supplier and contractors comply with IRPC’s Way of Conduct
- To develop and encourage Sustainability Management for suppliers and contractors
- To build and strengthen mutual business relationships with transparency
- To lower risks and increase supplier and contractor performance
In the overall supplier evaluation score, ESG factors have a total weight of 25%, where suppliers have to score at least 70% of total score.
Performance
Amount of Total Spending
| FY | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Total Procurement Spending (Billion THB) | 204.53 | 164.41 | 134.25 | 24.77 | 14.37 |
Spending on Local Suppliers for General Procurement
| FY | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
| Percentage of Local Spending to Total General Procurement Spending | 19% | 21% | 18% | 11% | 21% |
Total Number of General Procurement and Critical Suppliers
| FY | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 | 2023 |
| Total Supplier | 2043 | 1998 | 1979 | 2057 |
| Critical Tier 1 Supplier | 65 | 59 | 14 | 487 |
| Critical Non-tier 1 Supplier | 2 | 2 | 2 | 0 |
KPI for Supplier Screening
| FY 2022 | |
| Total number of Tier-1 suppliers | 2057 |
| Total number of significant suppliers in Tier-1 | 487 |
| % of total spend on significant suppliers in Tier-1 | 2 |
| Total number of significant suppliers in non Tier-1 | 0 |
| Total number of significant suppliers (Tier-1 and non Tier-1) | 487 |
KPIs for Supplier Assessment and Development
| Supplier Assessment | FY2022 | Target |
| Total number of suppliers assessed via desk assessments/on-site assessments | 487 | 100 % of significant suppliers |
| % of significant suppliers assessed | 100 | |
| Number of suppliers assessed with substantial actual/potential negative impacts | 0 | |
| % of suppliers with substantial actual/potential negative impacts with agreed corrective action/improvement plan | 0 | |
| Number of suppliers with substantial actual/potential negative impacts that were terminated |
0 |
Suppliers with corrective action plans
| Corrective action plan support | FY2022 | Target |
| Total number of suppliers supported in corrective action plan implementation | 0 | 100 % of significant suppliers |
| % of suppliers assessed with substantial actual/potential negative impacts supported in corrective action plan implementation | 0 |
Progress of suppliers in capacity building programs
| Capacity building programs | FY2022 | Target |
| Total number of suppliers in capacity building programs | 334 | 100 % of significant suppliers |
| % of significant suppliers in capacity building programs | 68.58 |



 Live Stream
Live Stream