Climate Strategy and Water Management
IRPC is committed to reducing our carbon footprint and building a sustainable future. We will invest in low-carbon technologies, promote circular economy practices, and support our communities. By setting ambitious targets and transparent reporting, we aim to be a leader in climate action.
Target
Support Low carbon society and sustainable roadmap to net zero
IRPC Commit to reduce emissions 20% by 2030
Achieve Carbon Neutrality 2050
Achieve Net Zero by 2060

Management Approach
IRPC recognizes the direct and indirect impacts of climate change throughout our businesses’ supply chain. IRPC has in place the climate change management approach by determining strategy, setting direction and reviewing strategy in accordance with the changes of situation, monitoring performance index regarding significant climate change. Energy Efficiency Index is set as an indicator for performance assessment among staff of all levels from the President to employees in the production line and supporting of related production lines. The performance is reported to the Board of Environmental Management, to the Management and the Board of Directors meeting. As for other indicator i.e., reduction of the greenhouse emission and water management which considered as an indicator for the operation unit, the result is reported to the Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee (Board level) and Management Committee (Executive level).
Policy
IRPC aims to reduce direct and indirect greenhouse gas emissions and water consumption in accordance with QSSHE Policy to carbon neutrality in 2050 and net zero by 2060 aligned with the Paris agreement to limit global temperature rise to well below 2 degrees Celsius by 3 GHG reduction program 1. Eco-operation & Technology (Shift the operation from fossil based power to renewable energy and increase energy efficiency) 2. Reshape-Portfolio (Adjust portfolio by investing in non-oil with Eco-Solutions) and 3. Absorption and offset (Seek all means to absorb and offset carbon) for low carbon society. IRPC, therefore, is committed to concerning the organization to SDG including climate change issues through IRPC Climate Change Statement.
IRPC Climate Change Policy [link]
Climate Change Governance
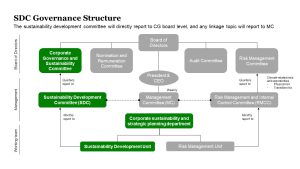
Climate Change Governance [LINK]
Management System/Process
Climate Change Risks and Opportunities Assessment
IRPC includes climate-related risks into its corporate risk portfolio and prioritizes risk portfolio by using risk matrix based on composite exposure of each corporate risks. The composite exposure is measured in 2-dimensions, Risk Likelihood and Risk Impact to an organization in 3 aspects (Economic, Social and Environment). This is for ensuring that we have well-balanced ESG risk portfolio.
IRPC has assessed climate change risks annually and determined sensitivity analysis of climate change risk in order to assess carbon dioxide reduction projects in order to consider cost and GHG reduction.
IRPC aim to develop our climate-related risk and opportunities assessments in alignment with recommendations from the Task force on climate-related financial disclosure (TCFD). Our assessments have been built upon the recent set of information reported in accordance with the requisites of Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET), as well as for the purpose of DJSI reporting requirements. This comprises of the following.
Physical Risks: altered weather pattern with more droughts and flooding, extreme weather events, resulting in increased business interruption.
Transition Risks:
- Policy and Legal: Thailand’s NDC target and policy, Thailand’s climate change act (draft) with corresponding of carbon taxation, and trading system for emission rights, encompassing risks from policy, targets, strategic plans, and laws stipulated by Thai government.
- Market: volatility of product price and demand shift in each scenario, refers to customers’ changing behavior, such as reduced fossil fuel demand.
- Technology: low-carbon technology or future energy that will replace fossil-fuel business such as renewable energy, electric vehicles and highly efficient batteries.
- Reputation: needs and expectations of investor which mostly concern about climate change management and transition to low-carbon business.
In 2024, we have conducted a report aligned with IFSR S2 standard and plan to disclose our climate-related risks and opportunities report. IRPC’s strategic approach to climate-related risks and opportunities is guided by a systematic process to enhance resilience and sustainability. IRPC has integrated climate considerations into the core business strategies and operational plans. By integrating scenario analysis, internal engagement, and risk management processes, it ensures a comprehensive response to climate challenges, driving forward-looking business strategies.
Climate Scenarios
From our risks and opportunities analysis, we have determined what would hypothetically happen to our businesses under two different scenarios as follows:
- STEPS (2.3°C) Scenario reflects current policy settings based on a sector-by-sector assessment of the specific policies that are in place, as well as those that have been announced by governments around the world. As a result of these collective actions, the global worming should be limited to around 2.8°C.
- NZE (1.5°C) scenariosets out a narrow but achievable pathway for the global energy sector to achieve net zero CO2 emissions by 2050, by which limiting global temperature rise no more than 1.5°C is expected to achieve this net zero target.
Our Responses to Climate–related Risks and Opportunities
| IRPC recognizes the importance of combating climate change by starting various organizational initiatives, like the Floating Solar Power project, Internal Carbon Pricing, and Carbon-Neutral project. IRPC is committed to develop products and organize initiatives that reduce greenhouse gas emissions to combat climate change. Moreover, IRPC also applies the circular economy principle to our business operations by collaborating with partners to reuse the industrial plastic waste in our production process. |
Quantifiable Opportunity
On the other hand, IRPC have also considered opportunities which might arise in the midst of climate change in order to stimulate the world’s agenda on limit temperature rise no more than 2°C. considering the change of consumers’ behavior towards EV cars, we find that the shift in new vehicle purchase in responding to the government promotion of the EV manufacturing would result in an increase in sales of petrochemical products, such as Polypropylene Compound & Composite which are used for the production of both interior and exterior automotive parts. Besides, to attain the needs of battery manufacturing, the supply of Acetylene will also be higher.
Task Force for Climate Related Financial Disclosure (TCFD) [link]
Climate Risks and Opportunities Report [link]
Climate-Related Management Incentives
To strengthen climate risk management, IRPC will integrate climate-related metrics into its corporate KPI framework. The CEO will be directly accountable for driving the company’s climate agenda through KPIs focused on greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions, net zero commitments, and energy intensity index.
This top-down approach will be cascaded throughout the organization. Executives from relevant functions will be assigned specific KPIs related to emission reduction and energy efficiency, ensuring accountability at all levels. These functional KPIs will be aligned with the overall corporate objectives and contribute to the achievement of IRPC’s climate goals.
By tying executive compensation and performance evaluation to climate-related metrics, IRPC aims to foster a culture of sustainability and drive tangible progress in mitigating climate risks.
Key elements of the incentive structure:
- CEO-level KPIs: GHG emissions, net zero commitment, energy intensity index.
- Functional-level KPIs: Emission reduction targets, energy efficiency improvements.
- Performance evaluation and compensation: Linked to achievement of climate-related KPIs.
- Organizational culture: Fostering a climate-conscious mindset and behavior.
This comprehensive approach will enable IRPC to effectively manage climate risks, enhance its sustainability profile, and contribute to a low-carbon future.
Corporate KPI [Link]
Related functional KPI [Link]
Climate Change Strategies
Discerning of the risks related to regulations, the climate change severity which is likely to increase in the near future, IRPC takes into account the Paris Agreement which Thailand has expressed its intention to lower the greenhouse emission to control the rising of the global temperature in 2016, the changes of market demand toward low-carbon products and the advance of low-carbon technology, for instance, batteries and electrified vehicles including physical risk i.e., severe weather, flood and the draught which could get worse. In other point of view, IRPC visions the opportunity of business growth through a variety of low-carbon products and the use of alternative energy of which IRPC has invested continuously in terms of product development and project implementation to manage such risks and to seek for an opportunity to become a leader of climate change management in a concrete plan. IRPC has established the climate change strategy and pathways as a framework for business operation as follows.

As IRPC recognize how importance of climate change impact on core businesses of oil and gas and petrochemical now facing, IRPC developed the climate change strategy and positioning the organization (as leader/ fast follower) to move forward. Process of strategy setting has been done through identifying risks & opportunities, evaluating peer practices & stakeholder expectations, and executive workshop. Our strategy aims to ensure that roadmap of initiatives should be undertaken to achieve its strategic ambition.
Sustainability Strategy endorsed by Board of Directors [Link]
Climate Change Strategy endorsed by Corporate Governance and Sustainability Committee [Link]
Net Zero Strategy endorsed by Board of Directors [Link]
Low Carbon Products
IRPC is committed to the research and development of new products to meet the different requirements from customers and development of environmental-friendly products which creates more business opportunity and helps IRPC to be able to adapt to the change in economy, society and environment, which leads to sustainable growth.
IRPC offers alternative solutions for users who are concerned about environmental impacts by developing the products as follows:
- POLIMAXX Green ABS, in which synthetic rubber is replaced by a natural rubber. The uses of product can reduce GHG emission.
- POLIMAXX Green PS, an innovative product made from 20-50% of styrenic mixed with natural rubber. The development of this product is a co-project between IRPC and a customer with the aim to develop a traffic cone made from plastic rubber composite which can reduce the use of synthesis rubber by 30%. The new traffic cone is strong, durable, flexible and impact-resistant.
- POLIMAXX Wood Plastic Composite is a plastic product with a mixture of wood powder, blending together outstanding properties of plastic and wood perfectly. IRPC focuses on developing products that can be used in consumer packaging and furniture. In case of consumer packaging, all requirements from Food Contact EU Regulation (FDA) had already been passed.
- POLIMAXX Natural Pigment Color Compound is categorized as an environmentally friendly plastic. It is developed by mixing plastic with natural color extracts instead of synthetic colors. The method does not compromise physical property of the plastic and is under international quality control. There are three colors, which are green from spinach, red from shellac, tomatoes, or strawberries, and yellow from turmeric, bell peppers, or carrots. This product is an alternative to the growing number of health and safety conscious consumers in Thailand and abroad.
- Products that have Carbon reduction label (HDPE, PP, PS and EPS) which applicable for various products, for instance, plastic bag, electrical appliance, heat insulation, etc. IRPC developed these products in term of energy saving and chemical usage reduction in the production process and registered Carbon Reduction Label.
- Gasohol
- Bio Diesel
- RMAXX L-Cement is a plastic product with mixture of cement for easy and quick cementation
- Bio-based Polystyrene product which is a mixture of Polystyrene plastic and flour
- P301K a product used in the plastic sheets of floating solar project which uses lower quantities of HDPE
In addition, IRPC also addresses the transition of a low carbon economy operating in their own operation through several projects. For example;
- Expandable Polystyrene (EPS) for Construction is the energy saving product for construction. It is a special heat insulation used in the construction of buildings that need temperature control.
- CHPI (Combine Heat and Power Project), which uses natural gas as a fuel and totally cancelled out the use of fuel oil boiler resulting in a reduction of carbon dioxide emission of more than 260,000 tons of carbon dioxide equivalent per year.
Emission Reduction
To contribute to the management of climate change, IRPC has improved the efficiency of the production process, develop low-carbon products and energy saving products. IRPC enhanced the energy efficiency in the production process continuously in order to utilize the natural resources to its maximum efficiency and bring about minimal impact to the environment. As a result of several production process improvements include efficiency improvement in heat and steam management, Electricity Reduction and Logistic Management, as well as collaborative initiatives with PTT Group, etc.
There are two types of energy saving and CO2 reduction program, which are operational control projects, and process improvement (includes additional equipment installation projects).
- Operational Control Projects, such as reduction of electricity consumption, reduction of internal heat loss and steam consumption in the operation process.
- Process Improvement Projects, such as equipment installation, electricity production facilities improvement.
Furthermore, IRPC invested 550 THB million in the Floating Solar Power project which has a generation size of 12.5 megawatts in 2020. Resulting in GHG reduction of approximately 10,510 tons of carbon dioxide per year.
Internal Carbon Pricing
In 2024, IRPC starts implement Internal carbon price at USD 20 per tonnes of CO2 equivalent as shadow pricing to evaluate new green investments and infrastructure projects. We have applied the ICP in Renewable projects and Energy Efficiency Improvements, example: Floating Solar Phase II for PP Plant and VDU Heater Energy Efficiency Improvement for Lube Plant. More than 12 projects using shadow pricing, for example Meltblown expansion project for Polypropylene, and Global Hygiene: Spun bond Expansion project for Polypropylene.
Water Management
IRPC establishes Sustainable Water Management Framework in order to ensure proper water management in IRPC supply chain, water risk assessment, and analyzing and developing risk mitigation plan.
IRPC initiates water consumption strategy 321RPSD which are
- 3R – Recycle, Reuse, and Reduce water consumption
- 2R – Reserve and Responsibility of water resource
- 1P – Public Participation for improving and managing water resource
- SD – Supply and Demand management for business continuity and ensuring no community conflict.
| IRPC recognizes the importance of setting up water-related targets and goals to align with public policies and meet the needs of surrounding communities
IRPC is committed to involving all stakeholders when managing water resource and its related impacts through programs engaging the authorities and surrounding communities, such as conserving water usage and water reserves in the case of droughts, distributing tap water, and planning flood prevention measures in local communities. As a member of Eastern Water War Room Management, IRPC also engages with governmental agencies (Royal Irrigation Department, Provincial Waterworks Authority, and Industrial Estate Authority of Thailand) in order to share and discuss resolution measures to water-related issues in the eastern region. Furthermore, IRPC is also involved with PTT Group Water Management Team: PTTWT in planning management strategies for efficient use of water resources in its production process. |
Water–related Risk Management Strategy
IRPC uses water from natural resource to feed into the production process. The water is allocated from Rayong Irrigation Department, released into quality improvement for use in various systems, including cooling water system, demineralized water production, using saltwater for Flue Gas Desulfurization (FGD). IRPC controls quality of water before discharging out of the premise under standard established by the Department of Industrial Works and other relevant authorities. Furthermore, to assure the effective use of water, IRPC has implemented the 3Rs principles to water management approach.
Water–related Risk Assessment
IRPC has the comprehensive risk management related to water, including physical risks i.e., water volume, water quality and risks related to regulations and provisions from risk assessment. According to the Aqueduct Water Tool of the World Resource Institute (WRI), it is found that IRPC is located in the low baseline water stress1. Consequently, the assessment result is brought forward for preparing water management plan and for the study and forecast on the use of water in the future business operation.
Remark: 1Baseline Water Stress means the ratio of water allocated for a certain area per total volume of water resource based on the water consumption of the upper basin area (resource: WRI Aqueduct 2014).
Water Management Risks [Link]



 Live Stream
Live Stream