Corporate Risk and Crisis Management
The Company recognizes the importance of risk management integration policy to ensure the Company's steady growth.

The Company recognizes the importance of risk management integration policy to ensure the Company’s steady growth with reduced or minimum damages caused by surrounding environmental and potential risks, which could have damaged the Company’s employees, assets, business operations, and reputation.
Executives and the employees are to adhere to the risk management policy so as to create awareness, collaborate, and streamline the risk management practices throughout the organization. Risk management processes and the level of manageable risk at an appropriate level are clearly defined, and in-line with the risk management strategies, action plans, and activity plans of all units. This includes such measures as continued risk assessments, review, enhancement, development of risk management process, as well as the annual review of risk management policy. Such measures aim to ensure the Company’s risk management process and policy are in place and able to respond positively to the changing business environment. The Company shall appoint the Risk Management Committee to oversee and manage the overall risk management of the organization, who are required to submit quarterly risk reports to the Audit Committee.
Management Approach
I. Policy
Risk Management Policy that covers the overall of organization risk management and systematically connects other management systems throughout the organization.
II. Responsible Organization
Corporate Risk Management, under Sustainability and Strategic Planning Department (CSSP) which separate from all business functions, has responsibilities in analyzing, monitoring and reporting progress and result of enterprise risk management. Although, the Corporate Risk Management is in CSSP but the control is fully belonged to Risk Management and Internal Control committee (RMCC) and the executive management level and Risk Management Committee (RMC). RMCC and RMC are responsible for overseeing the overall corporate risk management to ensure effectiveness of corporate risk management. RMCC and RMC chairs are held by the President and the Chief Executive Officer, and the Independent director respectively. Corporate Risk Management directly report to RMCC and RMC, the board of director level at least once a quarter. The benefit for Corporate Risk Management to be in CSSP would also help in assessing and managing risk since the planning of new strategies to achieve company’s goal.
The Board appointed the Risk Management Committee (RMC), consisting of 4 Board members with responsibilities to
- Formulate suitable, effective policy and give recommendations on the management of risks associated with IRPC’s business operations.
- Provide oversight for enterprise-wide risk management, starting with identification of risks based on internal and external factors. All units shall conduct risk assessment and rank those risks based on impact and likelihood of them happening, so appropriate risk management measures can be taken.
- Develop risk management systems and promote effective use of risk management tools, such as derivatives, futures and hedging, etc.
- Supervise, monitor and review the corporate risk management to ensure its effectiveness as well as assessing compliance with the risk management framework.
- Report risk management assessment results and risk mitigating activities to the Board on a regular basis, and in the case of risk event that may adversely affect IRPC’s operations, report to the Board immediately.
- Provide support for establishment and continuing development of risk management that is constantly in alignment with IRPC’s business plan.
- Give advice on risk management for investment projects or activities with considerable technical complications, long-term obligations, and are potentially exposed to significant risks.
- Disclose the report of the Risk Management Committee in the annual report.
- Perform other tasks assigned by the Board.
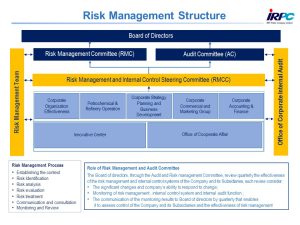

III. Management System/Process
The Company recognizes the importance of risk management integration policy to ensure the Company’s steady growth with reduced or minimum damages caused by surrounding environmental and potential risks, which could have damaged the Company’s employees, assets, business operations, and reputation.
Executives and the employees are to adhere to the risk management policy so as to create awareness, collaborate, and streamline the risk management practices throughout the organization. Risk management processes and the level of manageable risk at an appropriate level are clearly defined, and in-line with the risk management strategies, action plans, and activity plans of all units. This includes such measures as continued risk assessments, review, enhancement, development of risk management process, as well as the annual review of risk management policy. Such measures aim to ensure the Company’s risk management process and policy are in place and able to respond positively to the changing business environment. The Company shall appoint the Risk Management Committee to oversee and manage the overall risk management of the organization, who are required to submit quarterly risk reports to the Audit Committee.
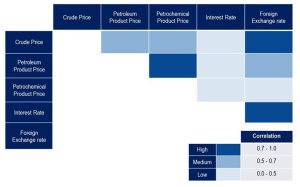
Risk Correlation The risk analysis was initially identified the correlation addressing the utmost impact to IRPC business, of which resulting in price volatility of raw materials and products as business risk and foreign exchange rate and Interest as financial risk. The statistically data from the previous 3 years have been considered and finding the mathematical equation correlation to forecast the future risk.
Sensitivity Analysis and Stress Testing
It is important to IRPC to implement internal control processes to comply with existing regulations and be proactive in developing their control mechanisms. Sensitivity analysis and stress testing is considered as part of an effective risk and crisis management. Sensitivity analysis and stress testing should be performed in order to better capture more extreme versions or more uncommon types of risks in addition to financial risk.
Emerging Risks
IRPC is aware of the long-term risks that company faces and the impacts of these risks on its business. IRPC shows its ability to identify risks that may arise in the next 3-5 years which will result in opportunity loss for the company if it is not appropriately managed. For this reason, IRPC has implemented assessment of the emerging risks such as risk from the changing free trade areas and trade rules.
Emerging Risks 1
Energy Technology Risk for Vehicles. Risk of a shift in consumer preference from internal combustion engine vehicles in favor of electric vehicles or those powered by other renewable energy, with improved technologies at lower price points. Diminishing EV range anxiety coupled with incentives offered by the government and the promotion of Thailand as a regional base for EV manufacturing, are driving electric vehicle demand. This will result in declining sales of IRPC’s fuel and lubricant products.
Risk management measures: The company has therefore formulated a long-term risk management plan with the strategy to gradually move away from petroleum products towards higher value-added petrochemicals, targeting Health & Life Science and Advanced Material segments along with emerging opportunities to tap into the plastic automotive parts and components that will raise the total added value of the company’s product lines.
Emerging Risks 2
Climate Change Risk: The increase in frequency and magnitude of natural disasters in recent years is linked to climate change, attributed mainly to human activities, particularly greenhouse gas emissions. At the latest summit of the United Nations Convention on Climate Change (COP27), Thailand delivered a progress report on the implementation of its long-term climate strategy. The Thai government reiterated its commitment to achieving Carbon Neutrality by 2050 and Net Zero Greenhouse Gas Emissions by 2065.
Risk Management Measures To meet Public sector’s policy and achieve national and international goals, as a part of Private Sector who has responsibilities and awareness of climate change risk, IRPC has targeted following goals: 20% reduction of CO2 emissions by 2030, Carbon Neutral by 2050 and Net Zero emissions by 2060, including studies on the application of Carbon Pricing in assessing the cost-effectiveness of future projects, putting in place measures to reduce GHG emission intensity, such as improving energy efficiency in its production processes, thereby reducing fuel combustion. IRPC has piloted a voluntary assessment as per the Carbon Footprint Organization (CFO) assessment guidelines in collaboration with the Department of Industrial Works and Thailand Greenhouse Gas Management Organization. (TGO), and implemented projects using solar panels to generate electricity, along with stepping up preparedness to export its products to countries that impose carbon tax under the Carbon Border Adjustment Mechanism (CBAM) in Europe.
Emerging risks are also shown in 2022 One Report, click
Risk Culture
Strong risk culture throughout the organization is a key to the development of an effective risk and crisis management. IRPC ensures that the importance of risk is understood and risk mitigation plans are well-followed by all employees through individual’s performance review, compensation, training on risk management principles, potential risk reporting mechanism for all employee, etc.
- Financial incentives which incorporate risk management metrics ;
For senior executives:
IRPC has in place dedicated Risk Management and Internal Control Committee (RMCC) to oversee implementation of risk management framework by managements and employees and continuously report the progress in board level Risk Management Committee (RMC). Management of corporate risk profile is directly linked to KPIs of the members of RMCC and RMC. KPIs are also deployed to the executives of relevant functions. Financial incentive is tied in with business performance and risk management performance using the KPIs, competency and desired behavior evaluate by PMS (Performance Management System). The company promotes risk management as an integral part of the corporate culture as well as instilling in its workforce a risk management mindset. Executives and personnel are expected to have good working knowledge and understanding of risk management systems relevant to their lines of work to achieve the objectives.
For management level:
Financial incentive is tied in with business performance and risk management performance using the KPIs. For Non-financial incentive, The company promotes risk management as an integral part of the corporate culture as well as instilling in its workforce a risk management mindset. Executives and personnel are expected to have good working knowledge and understanding of risk management systems relevant to their lines of work to achieve the objectives.
- Inclusion of risk management criteria in the HR review process for employee evaluations
IRPC prioritizes the importance of integrating risk management process into HR’s employee evaluation process. Setting the clear and concise risk management criteria help HR department to effectively evaluate, identify gaps and execute gap closing activity to ensure Human resource management excellence. IRPC has developed financial incentives which incorporate risk management metrics. For senior executives, financial incentive is tied in with business performance and risk management performance using the KPIs. The company promotes risk management as an integral part of the corporate culture as well as instilling in its workforce a risk management mindset. Executives and personnel are expected to have good working knowledge and understanding of risk management systems relevant to their lines of work to achieve the objectives.
- Incorporating risk criteria in the product development or approval process
During product development, IRPC take risks to achieve market success as well as to assess and address risks as early and affordably as possible and view risk mitigation as an integral part of the stages of product development. There are market-based risks such as commercial viability, customer acceptance, competitors, and the product introduction window timing that IRPC has focused on. Moreover, there are organizational risks like liquidity, availability of staff loading, and capability of project management, including the technical and logistical capabilities of supply chain and manufacturing partners, as well as the business stability of each. IRPC staff must be heavily involved with the selection, assessment, and interactions with supply chain and manufacturing partners during development.
- Measures allowing continuous improvement in risk management practices through the involvement of employees in structured feedback process.
Most of risk management measures in IRPC are inclusive of structured feedback process. For example, all the feedback, suggestions and comments from board of directors or executives for risk raised during risk management reporting session will be communicated to risk managers/risk owners and related parties. IRPC implemented “Functional risk criteria review process” that engage tolerance and level of care behaviors and encourage involvement of employees for improvement risk management practices.
- Measuring of Risk Culture Effectiveness
IRPC is in progress for developing Performance and Risk Management platform called “I-Risk program” that will support risk management process when dealing with larger scale of data available and summarize those data that will encourage openness and speed of response behavior in the risk culture. In addition, IRPC has developed the program for an effective risk culture. I-Risk is a risk management application for risk owner to identify risk event & treatment and regularly report to executives. The application was designed as a real time dashboard displaying risk statuses which provides real time risk surveillances and risk management monitoring. All users can get access to updated information on risk factors which are usually updated during the quarterly meetings.
- Focused training throughout the organization on risk management principles
IRPC has its annual enterprise risk management training as a requirement for all business units. Our main audiences are risk manager, risk owner and risk agents from those business units who will act as facilitators and change agents to support risk management activities within their business units. We set the enterprise risk management course annually training for all employees to build risk management awareness and culture.
IRPC organized series of risk culture promotion activities, e.g. compulsory risk trainings for risk managers in all departments, integration of risk criteria in the annual employee performance evaluation, integration of risk management performance indicators as a monetary incentive of executives. IRPC also appointed ERM Ambassador and ERM Auditor to assist in monitoring of risk management practices and promote good practices among employees. In addition, IRPC plans to organize formal trainings to raise awareness of risk management for 95% of all employees by the year 2020. IRPC carries out a Risk Control Self-Assessment for executives every 2 years in order to assess the risk awareness and application of risk management framework within the organization.
- Potential risks reporting throughout the organization
IRPC has many measures implemented to ensure “all the voice” is heard regards risk management. For example, there is monthly risk management reporting session, IRPC corruption mailbox (PO BOX 35) for reporting corruption risks. There are also Zero Accident Campaign including Process Safety Management (PSM) and Zero Process Safety Event (PSE), awareness from past events as known as Lesson Learned sending to all employee, Daily check-in in Line application for monitoring based location of employee to warning when being in risk zone, etc. It is clear that there is not only whistle blowing mechanism, but also every channels regarding to risk of all employee in every level reach to Corporate Risk Team.
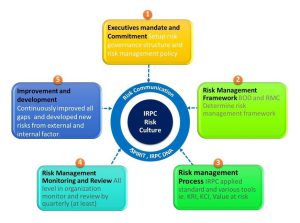
IRPC encourages and cultivates risk management to be a part of an organization culture. The culture embeds knowledge and understanding for the board of directors, managements, and employees on the importance and obligation for practicing standard risk management framework to allow IRPC to grow sustainably and firmly. IRPC has in place dedicated committee to oversee implementation of risk management framework by managements and employees and continuously report the progress in board level, management level, and operation level as well as improving and reviewing management approach in a timely manner. The committee is also responsible for communicating risks throughout the organization through various channels such as Board of Director’s meeting, Management Committee meeting, Function meeting, Operation meeting, Workshop training, E-mail notification, E-learning, ISPIRIT activities and IRPC DNA activities etc.
Regular Education on Risk Management for Non-Executive Directors
IRPC aims to promote and actively cultivate risk culture throughout the organization. Risk training is particularly important for IRPC to enable board for effectiveness in managing and addressing risks. Therefore, IRPC encourages the board continuing education on risk management by supporting them to participating risk training regularly at least once a year.
IRPC encourages the board continuing education on risk management by supporting them to participating risk training regularly at least once a year. IRPC’s directors regularly receive training from Stock Exchange of Thailand (SET) certified training such as Director Accreditation Program (DAP), Director Certification Program, and Thai Institute of Director Training. Non-executive director have attended new training sessions such as organized by the Thai Institute of Directors Association (IOD).
List of Board of Directors Training Courses relevant to Risk Management
- HOW TO DEVELOP A RISK MANAGEMENT PLAN
- RISK MANAGEMENT PROGRAM FOR CORPORATE LEADERS
- CORRUPTION RISK AND CONTROL WORKSHOP
Any risk issues according to changing of business environment such as law and regulation, technology, etc. will update information and educate to directors and executive officers.
Risk Management Process and Stress Testing [Click]
Climate Change Analysis and Sensitivity Analysis [Click]



 Live Stream
Live Stream